Value of Building Permits Slipped in May
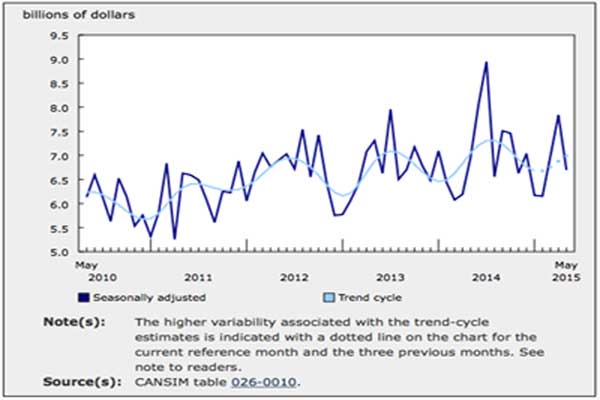
Following two months of double-digit gains in March and April, the total value of building permits issued in May fell 14.5% to $6.7 billion. Declines were recorded in five provinces, led by Ontario, which had posted a notable increase the previous month. The residential, industrial, institutional and commercial sectors were all affected.
Chart 1: Total value of permits
In the residential sector, the value of permits declined 13.5% to $3.9 billion in May, ending a string of three consecutive monthly increases. Declines were registered in seven provinces, with Ontario and Alberta responsible for much of the decrease. British Columbia, in turn, reported the largest gain.
Canadian municipalities issued non-residential building permits worth $2.8 billion in May, down 16.0% from April. This decline followed gains of 24.8% in March and 31.7% in April. Increases in seven provinces and one territory were not sufficiently large to offset decreases in the other provinces and territories. Ontario led the decline, followed by British Columbia and Newfoundland and Labrador.
Residential sector: Lower construction intentions for both multi-family and single-family dwellings
The value of multi-family dwelling permits fell for a second consecutive month, down 22.9% to $1.6 billion in May. The decrease stemmed from lower construction intentions in every province and territory, except British Columbia, New Brunswick and Nunavut.
Contractors took out $2.3 billion worth of building permits for single-family dwellings in May, down 5.5% from the previous month. This was the third decline in four months. Decreases were posted in five provinces, with Ontario recording the largest decline, followed by Alberta, a distant second. Quebec registered the largest gain.
Nationally, municipalities authorized the construction of 15,381 new dwellings in May, down 14.8% from April. The decrease came mainly from multi-family dwellings, down 20.6% to 9,719 units. The number of single-family dwellings declined 2.8% to 5,662 units.
Chart 2: Residential and non-residential sectors

Non-residential sector: Large decline in the institutional component
The value of permits for institutional buildings fell 34.0% to $867 million in May, after posting gains of 83.7% in March and 88.1% in April. The decrease at the national level resulted from lower construction intentions for medical facilities, which recorded a large increase in April. Declines were registered in four provinces, with Ontario accounting for most of the drop, followed by British Columbia. Gains were posted in the six remaining provinces, led by Alberta, and were mainly the result of higher construction intentions for educational facilities.
In the industrial component, construction intentions fell 15.6% to $408 million in May, following three straight monthly advances. The decline originated from lower construction intentions for utilities buildings and transportation-related buildings. Declines were reported in six provinces, led by Ontario and Newfoundland and Labrador. Alberta and Quebec posted the largest gains
Commercial building permit values totalled $1.5 billion in May, edging down 0.4% from a month earlier. Lower intentions for retail complexes, hotels and restaurants, warehouses as well as other minor commercial projects more than offset increased intentions for recreational buildings, office buildings and laboratories. British Columbia registered the biggest decline, while Quebec recorded the largest increase.
Permit values down in five provinces
The total value of building permits declined in five provinces in May, with Ontario posting the largest decrease, followed by British Columbia, Alberta, Newfoundland and Labrador and Nova Scotia.
After reporting the largest increase the previous month, Ontario posted a decline, mostly as a result of lower construction intentions for institutional buildings, multi-family dwellings and single-family houses. In British Columbia, the decrease originated from commercial structures, institutional buildings and single-family dwellings.
In Alberta, the decline was mostly attributable to multi-family dwellings, single-family houses and commercial buildings. In Newfoundland and Labrador, lower construction intentions for industrial buildings explained much of the decline, while in Nova Scotia, lower intentions for multi-family dwellings were responsible for the decline.
In contrast, Quebec and New Brunswick registered the largest increases. In Quebec, the increase came from higher construction intentions for non-residential buildings and single-family dwellings. In New Brunswick, the gain was attributable to every component, except industrial buildings.
Lower construction intentions in almost half of the census metropolitan areas
In May, the total value of permits fell in 16 of the 34 census metropolitan areas, with Toronto posting the largest decline, followed by Calgary and Vancouver.
In Toronto, the decline originated from institutional buildings and multi-family dwellings. Both components were up notably the previous month. In Calgary, lower construction intentions for multi-family dwellings and, to a lesser extent, industrial buildings and institutional buildings were responsible for the decline. In Vancouver, commercial and institutional buildings accounted for much of the decrease.
In contrast, Hamilton and Edmonton posted the largest gains. In Hamilton, the advance was attributable to higher intentions for institutional buildings, while in Edmonton, increased construction intentions for multi-family dwellings, institutional structures and industrial buildings more than offset lower intentions for single-family dwellings and commercial buildings.
Source: Statistics Canada, http://www.statcan.gc.ca/daily-quotidien/150708/cg-a001-eng.htm.










![Guide to the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1[i], 26th Edition – A Road Map: Section 10 – Grounding and Bonding](https://electricalindustry.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Guide-CE-Code-2.png)