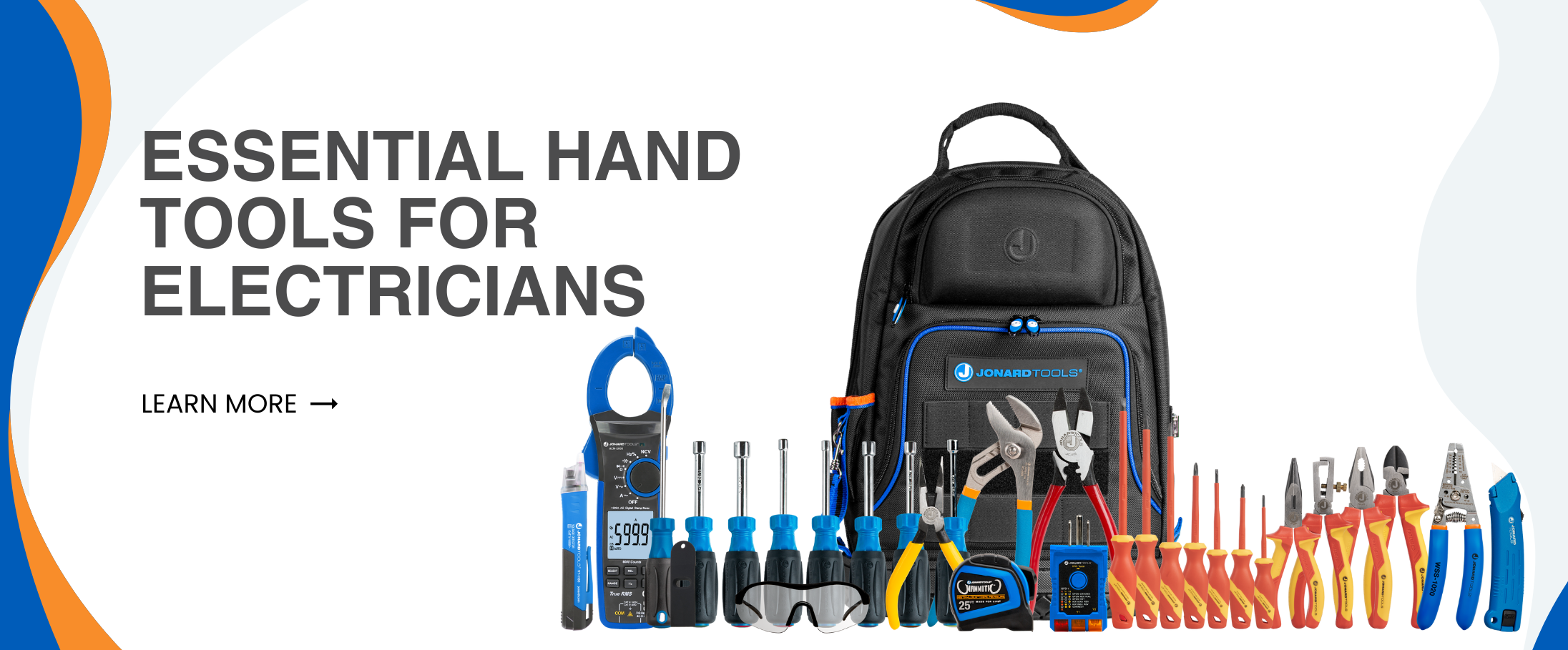
A Guide To The Most Essential Hand Tools for Electricians
February 22, 2024
By Jonard Tools
It is currently a great time to be an electrician- however, you’ll need the right hand tools for the job. In this article Jonard Tools highlight the most essential hand tools for electrical work, as well as dive into the specifics of how they are utilized and why they’re important.
Pliers
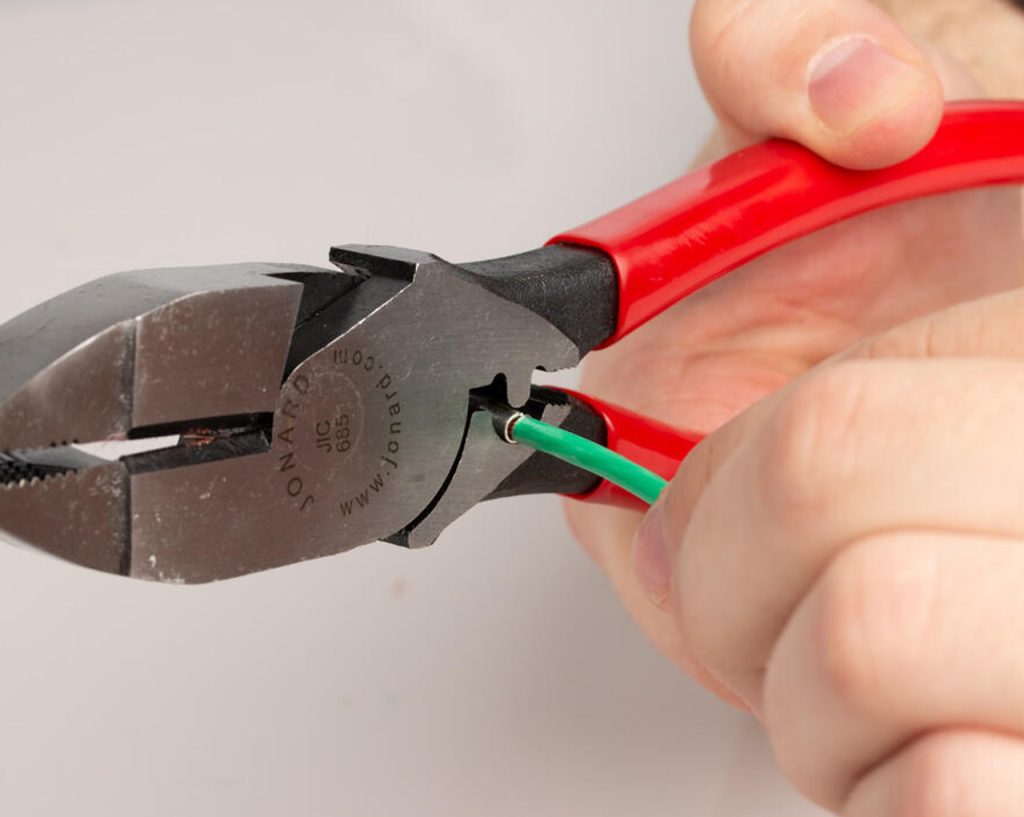

To start off the list, we have our trusty pliers! Pliers are some of the most common and versatile tools used for a variety of tasks in electrical installation and maintenance. Here are some of the most essential pliers along with their uses:
Long-Nose Pliers: Long-nose pliers are useful for bending and shaping wires, especially when you need to route wires neatly within electrical enclosures or tight spaces. They’re also utilized for gripping and positioning components.
Diagonal Cutters: These pliers are used to cut wires, especially when trimming excess wire after making connections. They’re designed with sharp jaws that can cleanly cut through wire without damaging the surrounding insulation.
Pump Pliers: A pump plier is a type of adjustable plier with serrated jaws and an adjustable pivot point. It’s designed for a wide range of gripping, holding, and turning tasks, particularly when dealing with objects of varying sizes. The name “pump plier” comes from the action of the handles resembling the motion of a pump handle.
Plier with Fish-Tape Puller: A plier with a tape puller is a specialized tool that combines the functions of traditional pliers with a built-in mechanism to assist in pulling wires or cables through conduits, pipes, or other tight spaces. This tool is particularly useful for electricians who need to route wires or cables through challenging pathways.
Testers
Voltage Tester
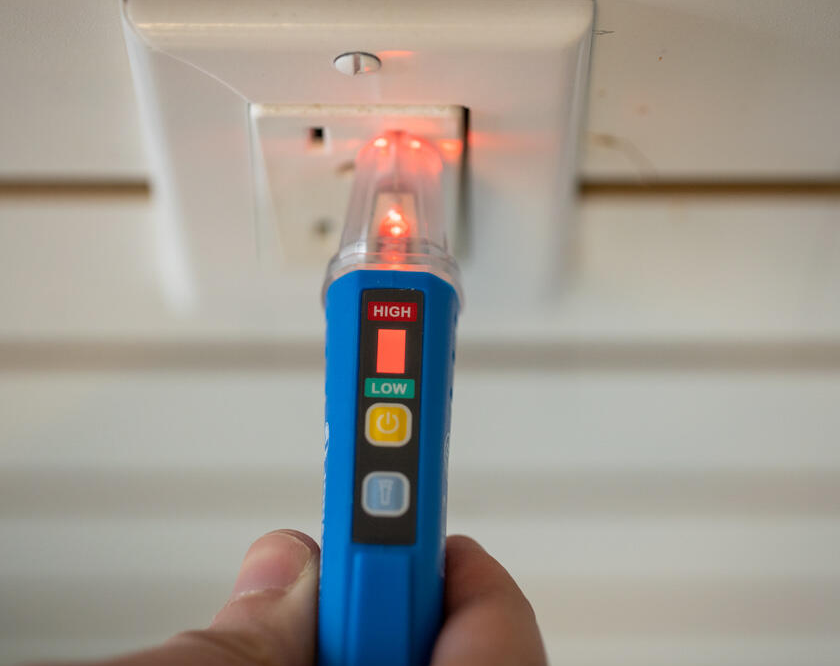

A Voltage Tester is a crucial tool for electrical work because it allows electricians and technicians to determine the presence or absence of electrical voltage in a circuit/electrical device. Here are some reasons why voltage testers are important for electrical work:
Verifying circuit status: Whether during installation or repair, electricians need to verify if a circuit is live or not. A voltage tester provides a quick and straightforward method to confirm the status of a circuit, avoiding any confusion or potential mistakes.
Troubleshooting: When diagnosing electrical issues or faults, a voltage tester helps electricians identify the faulty areas of a circuit/electrical device. By testing voltage at different points in the circuit, they can pinpoint the source of the problem, such as a broken wire, a faulty component, or an incorrect connection.
Safety: Safety is the most critical reason for using a voltage tester. Before working on any electrical circuit or device, it’s essential to ensure that no voltage is present. A voltage tester helps identify live wires or circuits that could pose a risk of electric shock or injury. It allows electricians to take necessary precautions or de-energize the circuit before starting work.
GFCI Outlet Tester
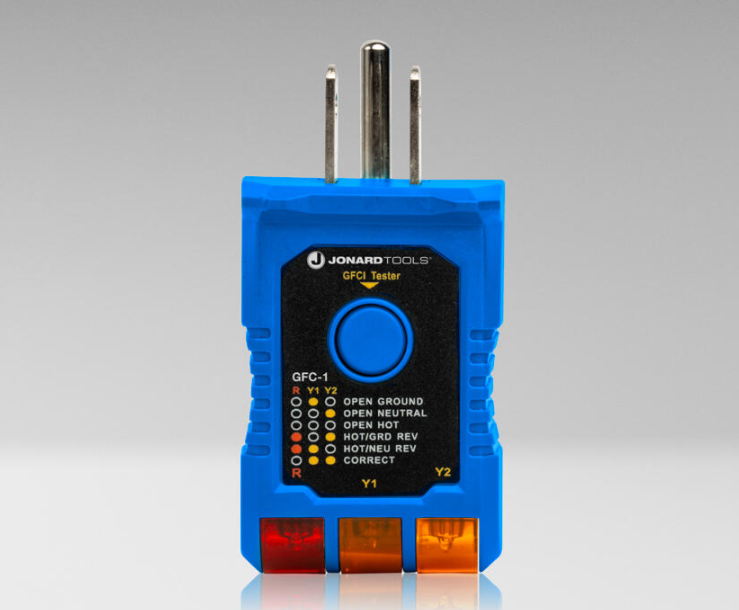

A GFCI outlet tester is a specialized device used to test the functionality of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets or circuits. As electrical safety devices, they are designed to protect against electric shock by quickly shutting off power to a circuit if it detects a difference in current between the hot and neutral wires, indicating a leakage or fault to ground. They have a myriad of functions, such as:
Function Testing: The primary use of a GFCI tester is to check if a GFCI outlet or circuit is functioning properly. When plugged into an outlet, the tester simulates a ground fault and verifies whether the GFCI responds by quickly cutting off power.
Verification of Wiring Correctness: GFCI outlets are often installed with specific wiring configurations to ensure proper operation. A GFCI tester can help verify if the wiring is correct and the GFCI is properly connected.
Periodic Testing: It’s recommended to test GFCI outlets regularly to ensure they are working as intended. GFCI testers allow for convenient and routine testing of multiple outlets without the need for specialized equipment.
Screwdrivers
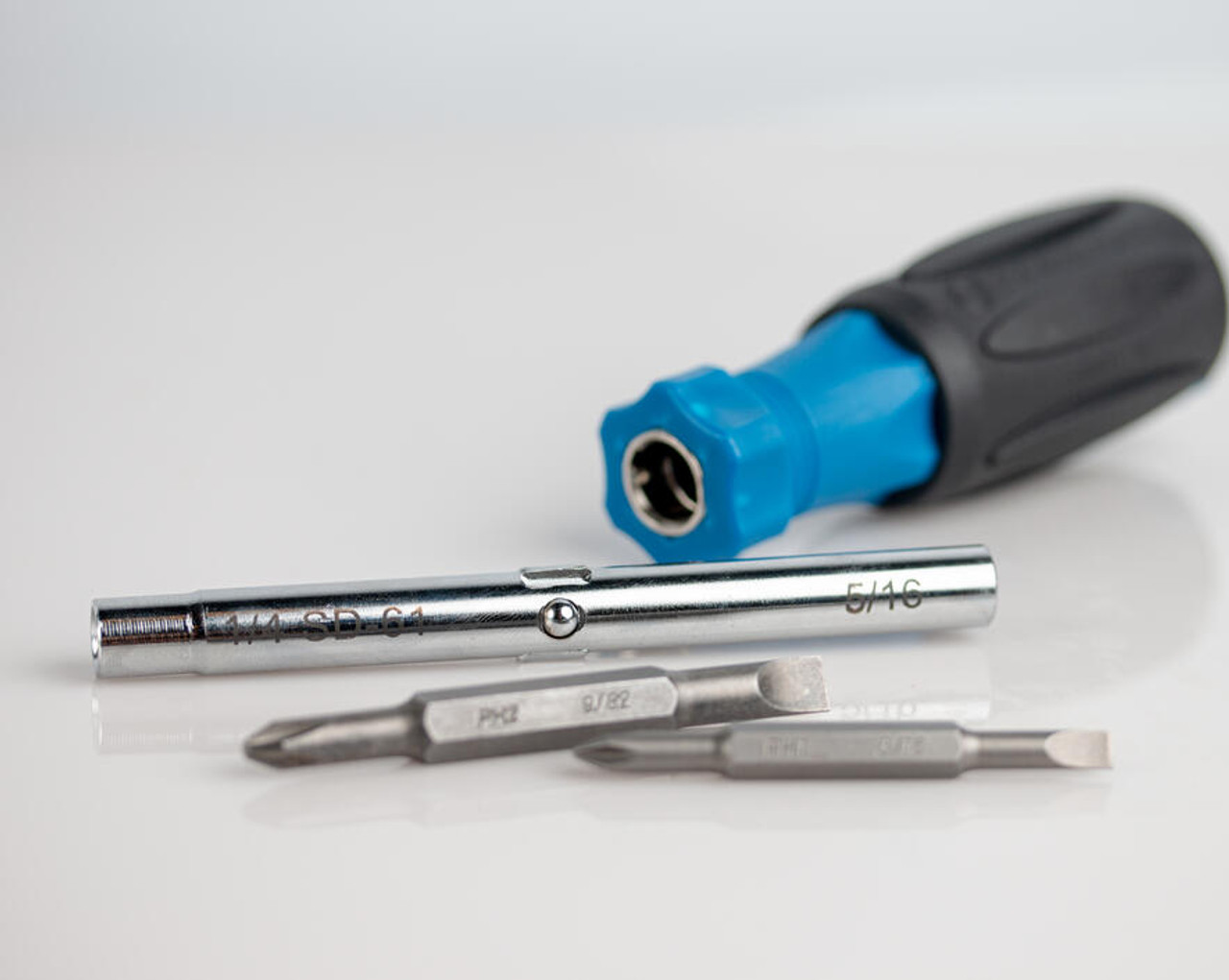

Screwdrivers play a crucial role in various tasks related to installing, maintaining, and repairing electrical systems and devices. These are some of the most essential screwdrivers for electricians:
Flat-Head Screwdriver (Slotted Screwdriver): This is one of the most common screwdriver types, with a flat, straight blade that fits into slotted screw heads. It’s used for tightening or loosening screws with a single slot across the head. They’re commonly used in general household tasks.
Phillips Screwdriver: The Phillips screwdriver has a cross-shaped tip and is designed to fit into Phillips screw heads. These screws have a cruciform indentation and are often used in a wide range of applications, from electronics to woodworking.
Hex Screwdriver (Allen Key): A hex screwdriver, also known as an Allen key or wrench, has a hexagonal-shaped tip. It’s used with hex socket screws commonly found in furniture, machinery, bicycles, and more.
Tape Measure
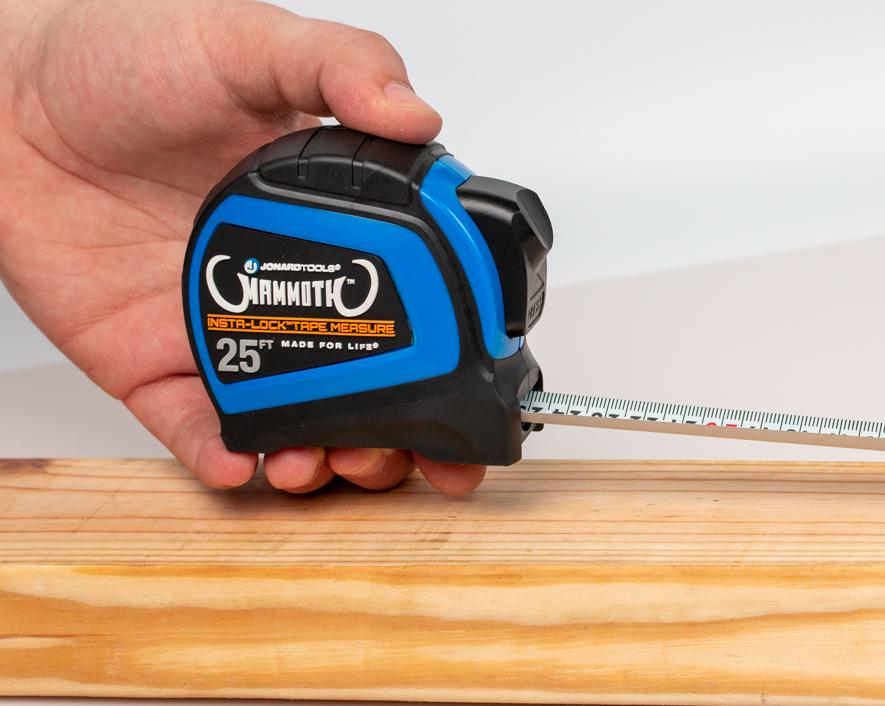

Tape Measures are important tools due to their versatility, accuracy, and ability to measure distances precisely. They play a crucial role in various tasks related to electrical installations, wiring, and equipment positioning. Here are some reasons why tape measures are important for electrical work:
Measuring distances: Electrical work often requires precise measurements to ensure proper spacing between components, fixtures, outlets, and conduits. Tape measures allow electricians to measure lengths accurately, helping to avoid errors and ensure the electrical system’s integrity.
Planning and layout: Before starting any electrical installation, electricians need to plan the layout of the system carefully. Tape measures help in designing and marking where fixtures, outlets, and other electrical components should be placed for optimal functionality and aesthetics.
Conduit sizing: Conduits are used to protect and route electrical wires. Electricians use tape measures to determine the appropriate conduit length needed for specific runs, ensuring that the wires fit securely and safely within the conduit.
Portable and easy to use: Tape measures are portable and can be easily carried around in a tool belt or pocket, making them convenient for on-site measurements during electrical work.
Utility Knife
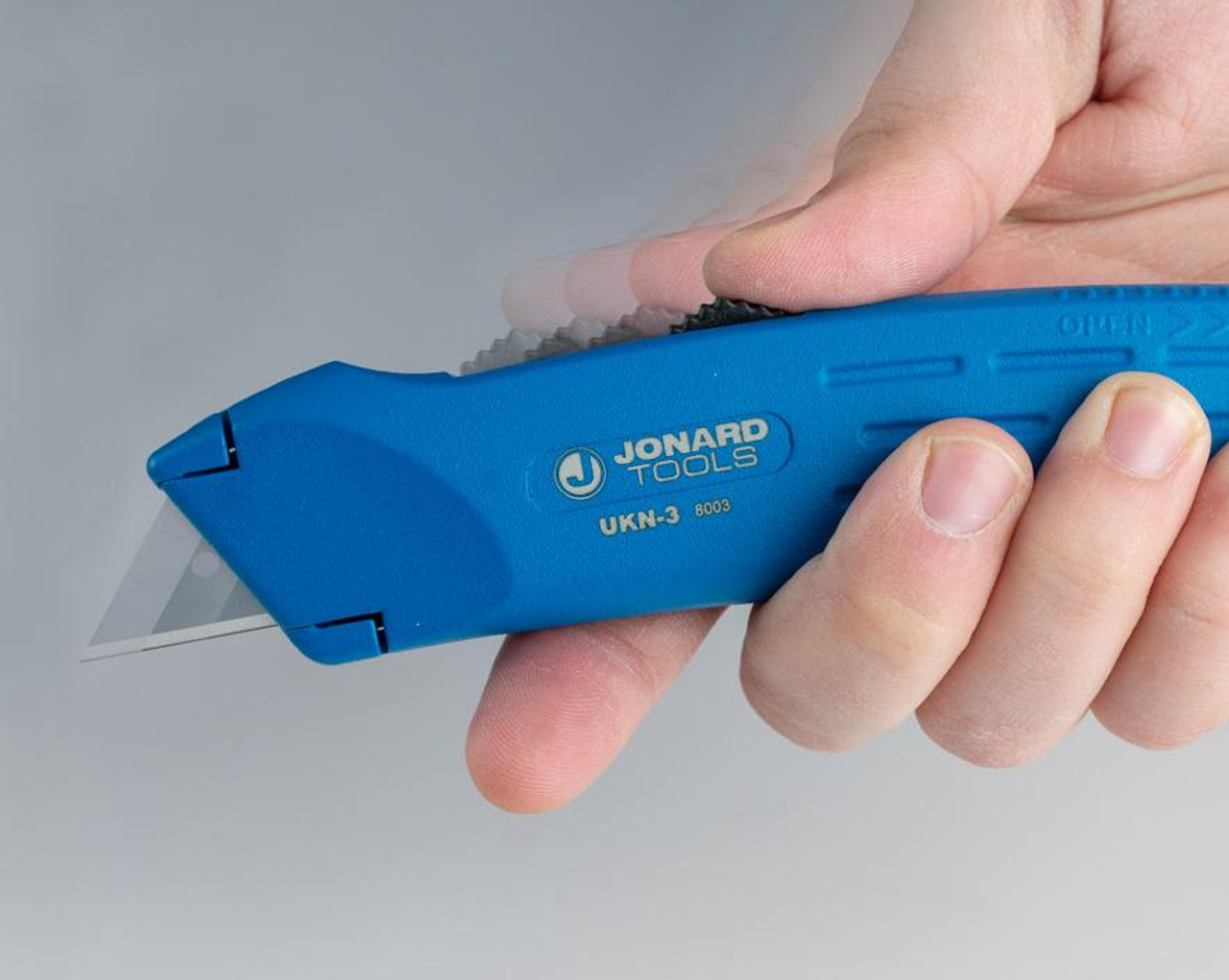

A Utility Knife is an important tool for electrical work due to its precision in various tasks related to cutting and stripping material. Here are some of the popular uses:
Cutting wires and cables: A utility knife with a sharp blade allows electricians to cut through electrical wires and cables cleanly and efficiently. This is essential for creating precise wire lengths and ensuring a neat and organized wiring system.
Stripping wire insulation: Many utility knives have a built-in wire stripper feature. Electricians can use this feature to strip the insulation from the ends of wires quickly and accurately, exposing the conductors for proper connections.
Removing cable jackets: Utility knives can be used to slit and remove the outer jackets of cables, revealing the individual wires inside. This is particularly helpful when dealing with multiconductor cables or larger electrical cables.
Trimming conduit and tubing: Electricians often work with conduit and tubing to protect and route electrical wires. A utility knife allows them to trim conduit and tubing to the required lengths easily, ensuring a proper fit for the wires.
Wire Stripper/Cutter
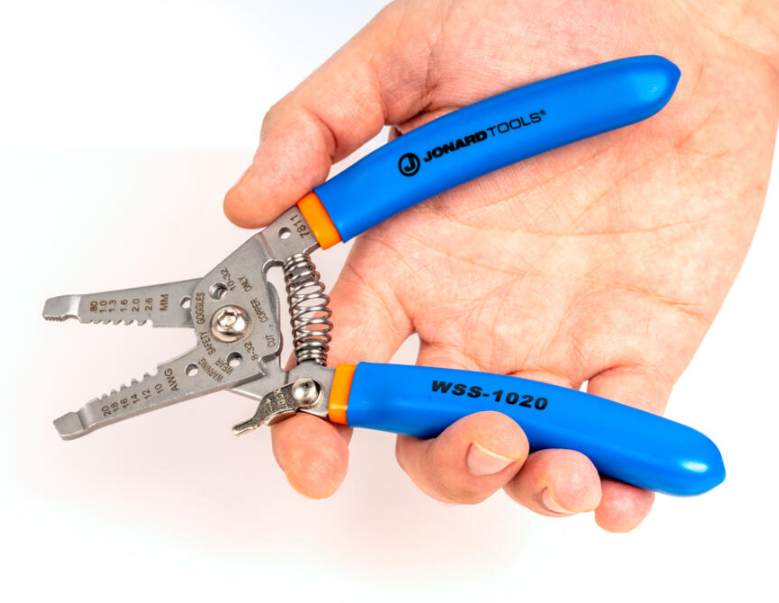

A wire stripper is a handheld tool designed to remove insulation from electrical wires and cables while also having the capability to cut the wire itself. It is a versatile tool commonly used in electrical work, electronics, and various applications where working with wires is involved. Its uses include, but are not limited to:
Stripping Insulation: The primary purpose of a wire stripper is to remove the insulation from the ends of electrical wires. This exposes the conductive metal, allowing the wire to be connected to terminals, connectors, or other components.
Cutting Wires: The cutting edges of the tool are used to cut wires to the desired length. This is especially useful when preparing wires for connections or when trimming excess wire.
Crimping and Terminating: Some wire stripper/cutter models include crimping jaws or additional features that allow them to crimp connectors onto wires, creating secure and reliable electrical connections.
Nut Drivers
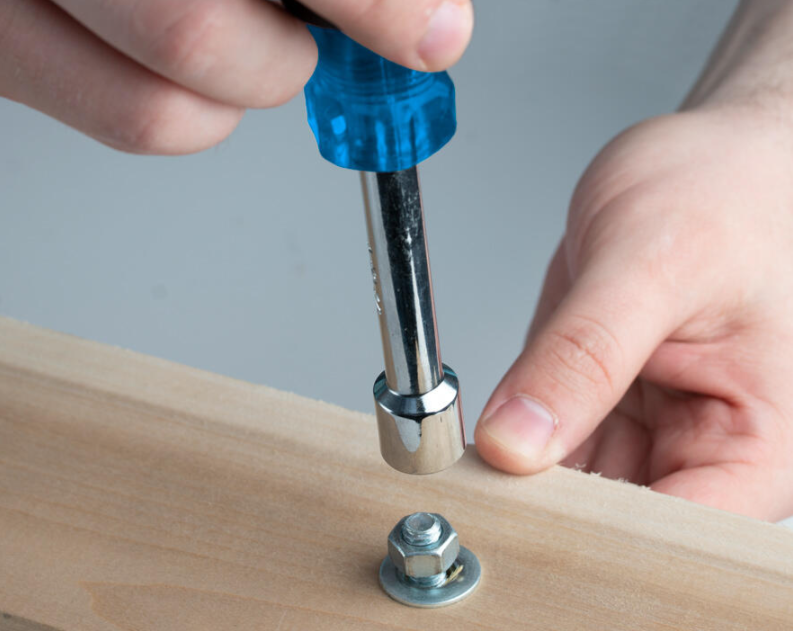

A nut driver is an important hand tool designed for driving nuts and bolts. They have a cylindrical or hexagonal-shaped socket at one end that fits over the nut or bolt head, allowing for turning and tightening. Here are some key functions of nut drivers:
Tightening terminal screws: Electrical components, such as switches, outlets, and circuit breakers, often have terminal screws that need to be tightened securely. Nut drivers provide a precise and controlled way to tighten these screws to the manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring a reliable electrical connection.
Connecting Wires: Nut drivers are commonly used to secure wires together within junction boxes or electrical enclosures. They are especially useful for connecting wires to wire connectors (wire nuts) or terminal blocks. The nut driver ensures a tight and secure connection, preventing loose or exposed wires that could lead to electrical hazards.
Assembling electrical panels: In the construction of electrical panels and control cabinets, nut drivers are used to secure various components, including circuit breakers, relays, and bus bars. Proper torque is essential in these applications to prevent overheating and maintain the integrity of electrical connections.
Grounding and bonding: Nut drivers are vital for establishing grounding and bonding connections in electrical systems. They are used to secure grounding clamps, lugs, and connectors to grounding electrodes or conductors, ensuring a safe path for electrical fault currents to dissipate harmlessly into the earth.
Protective Eyewear
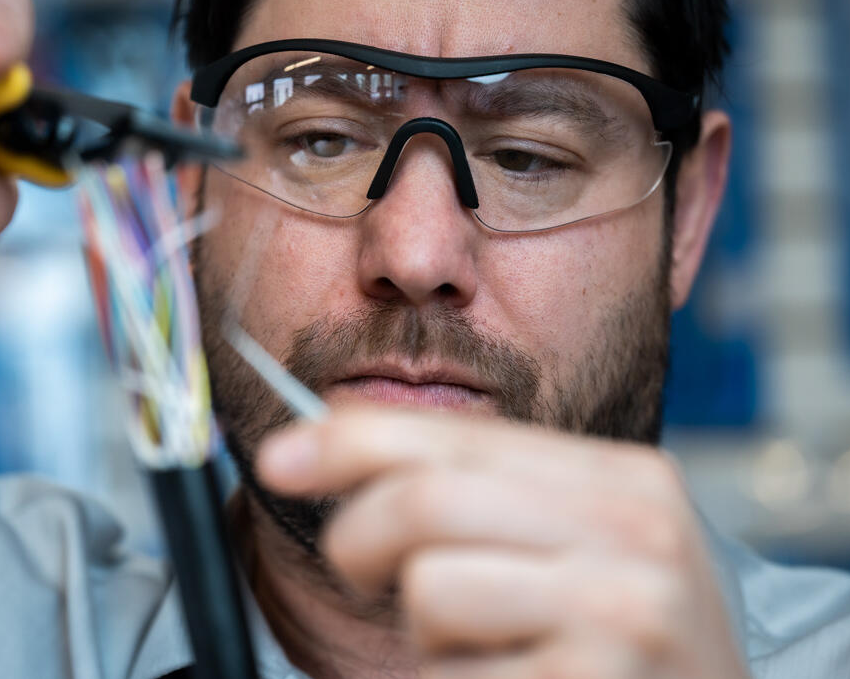

Protective Eyewear is crucial for electrical work due to the potential hazards and risks associated with the tasks involved. Here are some reasons why protective eyewear is necessary:
Safety from Arc Flash: Electrical work can involve the risk of arc flashes or electrical explosions, which release intense heat, light, and debris. Protective eyewear with impact-resistant lenses helps shield the eyes from flying particles and debris generated during an arc flash.
Protection from Sparks and Debris: Working with electrical components, wiring, and equipment can create sparks, especially during cutting, stripping, or splicing wires. Protective eyewear helps prevent sparks and small debris from entering the eyes, reducing the risk of eye injury.
Chemical Exposure: Some electrical work may involve using chemicals such as solvents, adhesives, or cleaning agents. These chemicals can cause eye irritation or injury if they come into contact with the eyes. Protective eyewear provides a barrier against chemical splashes.
Falling Objects: In construction or maintenance work, tools, equipment, or materials can accidentally fall from heights, potentially causing eye injuries. Proper eyewear with impact protection can help safeguard against these incidents.
UV Radiation: Welding and certain electrical processes emit ultraviolet (UV) radiation that can harm the eyes. Proper protective eyewear may include lenses that provide UV protection to reduce the risk of damage to the eyes.
Clamp Meter
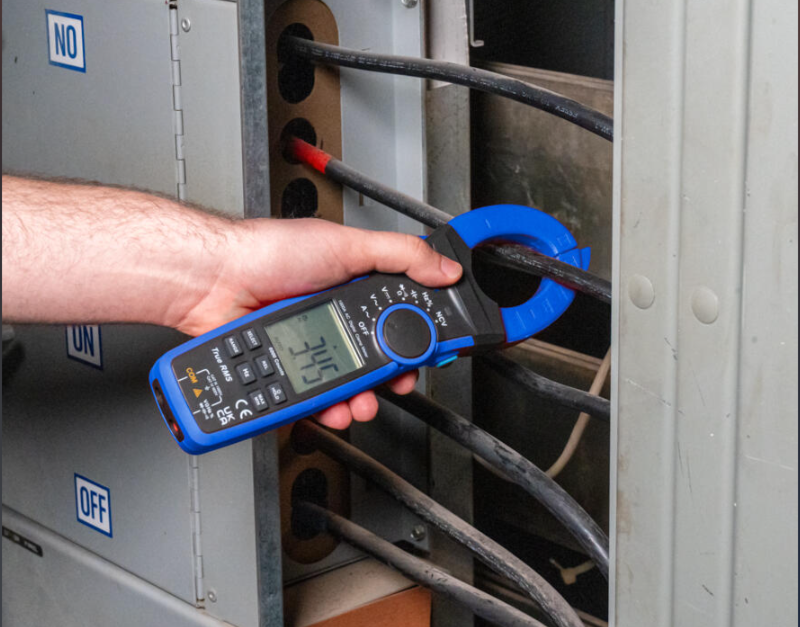

A clamp meter is a specialized handheld electrical testing tool used for measuring electrical current in a conductor without the need to disconnect or interrupt the circuit. It is a valuable instrument for electricians, technicians, and maintenance professionals. Here are some of the fundamental uses of clamp meters:
Non-Contact Current Measurement: One of the primary functions of a clamp meter is to measure electrical current in a conductor without physically touching or breaking the circuit. It achieves this by using a hinged jaw-like clamp that can be clamped around the conductor. This non-contact feature makes it particularly useful for safely measuring current in live electrical systems without the risk of electrical shock or circuit interruption.
Versatile Current Measurements: Clamp meters are capable of measuring both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). They can measure a wide range of current values, from milliamps (mA) in low-power electronic circuits to hundreds of amps (A) in industrial and commercial applications.
Additional Measurements: Many modern clamp meters are equipped with additional measurement functions, such as voltage, resistance, capacitance, and frequency. This versatility allows electricians to perform multiple electrical tests with a single tool.
Applications: Clamp meters are used in various applications, including troubleshooting electrical circuits, assessing the current draw of electrical devices, verifying the proper operation of electrical systems, and diagnosing electrical issues in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. They are especially useful for measuring current in tight or hard-to-reach places where traditional current measurement methods may be impractical.
Drywall Saw

A drywall saw is a handheld tool that features a serrated blade designed for cutting through drywall, plasterboard, and similar materials. While a drywall saw is not a tool directly related to electrical work, it can be valuable for electricians in certain situations. Here’s why a drywall saw is sometimes necessary for electricians:
Access to Wiring: Electricians often need to run electrical cables and wires through walls and ceilings. A drywall saw allows them to create precise openings in drywall or plasterboard to access the cavities where wiring needs to be installed. This can include creating holes for outlets, switches, junction boxes, and conduit.
Retrofitting or Upgrades: When adding new electrical outlets, switches, or lighting fixtures to existing structures, electricians may need to cut openings in drywall to install new electrical boxes or conduit pathways. A drywall saw helps them create clean and accurate cutouts.
Inspection and Troubleshooting: When diagnosing electrical issues within walls or ceilings, electricians may need to make exploratory cuts to inspect wiring, connections, or possible problems. A drywall saw enables them to access the area without causing extensive damage.
Cable Routing and Fishing: In some cases, electricians need to route cables or wires from one location to another through existing walls or ceilings. A drywall saw allows them to create channels or paths for the wires to pass through while minimizing damage to the surrounding drywall.
Fixture Installation: Installing fixtures like ceiling fans, light fixtures, and smoke detectors often requires creating openings in the ceiling or wall. A drywall saw makes it easier to create precise cutouts for mounting brackets and connections.
Access Panels: In commercial or industrial settings, electricians may need to create access panels in drywall to reach utility panels, control systems, or equipment behind walls for maintenance and repairs.
Tool Bag
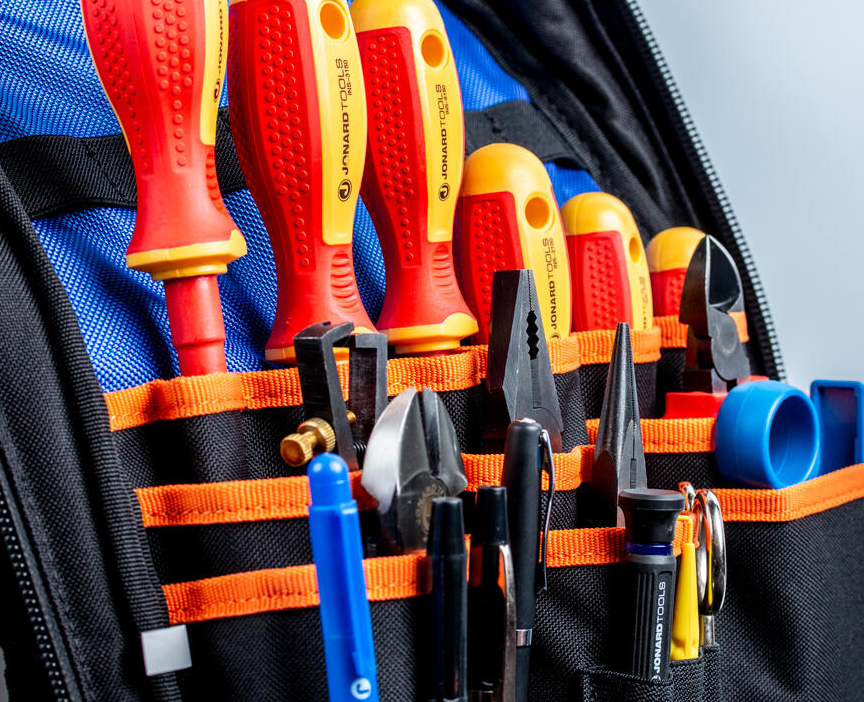

Last, but certainly not least, an electrician will need a way to carry, organize, and protect all of these tools. For that purpose, they will need a tool bag. Here are some of the important functions of a tool bag:
Organization: As we have now learned, electricians use a wide range of tools in their work, including screwdrivers, pliers, wire strippers, voltage testers, and wrenches. A tool bag provides separate compartments and pockets, enabling electricians to keep their tools organized and easily accessible.
Portability: A tool bag allows electricians to carry their essential tools from one job site to another conveniently. It’s designed to be portable and can be carried over the shoulder or by hand, making it easy for electricians to transport their tools as they move around during work.
Protection: Electrical tools can be expensive and delicate, and a tool bag provides a protective barrier against potential damage. The bag’s material and padding help prevent tools from getting scratched, dented, or exposed to harsh environmental elements.
Quick identification: A tool bag usually has multiple compartments and may include transparent or labeled pockets, making it easier for electricians to identify and locate the specific tool they need without wasting time searching.
Safety: Some electrical tools, such as voltage testers and insulated screwdrivers, require specific safety precautions when not in use. A tool bag can help keep these tools safely enclosed, reducing the risk of accidental contact with live electrical components.
Professionalism: Carrying a tool bag gives electricians a professional appearance and helps create a positive impression on clients. It shows that the electrician is well-prepared and takes their work seriously.








![Guide to the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1 – 26th Edition[i] – A Road Map: Section 54](https://electricalindustry.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Guide-CE-Code-2-768x432.png)








