Canadian Electricity Generation in January up 1.5%Year Over Year
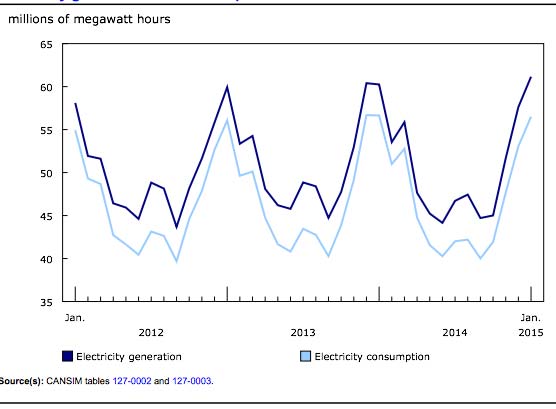
Canada generated 61.2 million megawatt-hours (MWh) of electricity in January, up 1.5% from January 2014. The increase was a result of higher generation levels in Quebec, Manitoba, Ontario, and Newfoundland and Labrador. Exports of electricity to the United States rose by 11.8% to 5.4 million MWh, while imports fell 37.2% to 0.8 million MWh, influenced by the strong appreciation of the U.S. dollar against the loonie. While generation increased, the rise in net exports of electricity resulted in a 0.2% decline in available electricity (56.5 million MWh) in Canada.
Chart 1: Electricity generation and consumption
The major contributors to the decrease in domestic demand were British Columbia (-4.2%) and Alberta (-4.5%). In British Columbia, generation declined 0.9% to 6.2 million MWh as a result of lower production from combustion turbine and conventional steam power plants. As well, the province purchased less electricity from other provinces and the United States while increasing sales south of the border. Alberta’s drop in demand contributed to a 5.2% decrease in generation to 5.6 million MWh.
Tempering the decline in national demand were New Brunswick and Ontario. In New Brunswick, demand for electricity rose 10.5% above January 2014 levels to 1.8 million MWh. Colder than normal temperatures in the Atlantic province, where electricity is the primary heating source, contributed to the rise in demand. While generation levels edged down 0.4% to 1.6 million MWh on a year-over-year basis, the supply was supplemented by increased receipts of electricity from Quebec and lower exports to the United States.
Demand for electricity rose 1.0% in Ontario to 11.0 million MWh in January. To meet the increase, electric power generation rose 2.0% to 13.5 million MWh on the strength of rising nuclear power generation.
Source: Statistics Canada, http://www.statcan.gc.ca/daily-quotidien/150325/dq150325c-eng.htm?cmp=mstatcan.





![Guide to the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1[i], 26th Edition– A Road Map: Section 56](https://electricalindustry.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Guide-CE-Code-2-768x432.png)




![Guide to the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1[i], 26th Edition– A Road Map: Section 56](https://electricalindustry.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Guide-CE-Code-2.png)



